Products
News
- How to Install AAC Conductor
- Power cable current carrying capacity
- Guide on Low Voltage Aerial Bundling Cables(ABC Cab
- Guide to Electrical Insulators
- The difference between 3 + 2 and 4 + 1 on wires and
- What are the cable accessories?
- AWG (American Wire Gauge) to MM2 Conversion
- Cable Short Circuit Current Calculate
- Overhead conductor,poles,and gold fittings design
- OPGW Cable Line Design Several Key Issues[2]
Contact us
E-Mail:info@dosensecable.com
Phone:+8613073786551
Tel:+8613073786551
Add:Zhengzhou, Henan,China
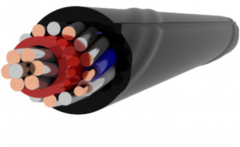
Medium Voltage Cable Heat Shrink Terminals
Brand:Dosense Cable
Category:Products
Materials Used in Medium Voltage Cable Heat Shrink Terminals: Heat Shrinkable Tubing: This is the main component of the terminal and provides insulation and sealing. Its typically made from cross-linked polyolefin or other heat shrinkable p...
Materials Used in Medium Voltage Cable Heat Shrink Terminals:
Heat Shrinkable Tubing: This is the main component of the terminal and provides insulation and sealing. It's typically made from cross-linked polyolefin or other heat shrinkable polymers.
Adhesive: The heat shrink tubing often includes an adhesive lining that melts and flows when heated, forming a tight seal around the cable and conductor.
Stress Control Tubes: These are used to evenly distribute electrical stress and prevent corona discharge at the interface between the cable insulation and the terminal.
Mastic: Mastic is a viscous sealing material applied to enhance moisture resistance and provide additional insulation. It's often used in conjunction with stress control tubes.
Insulating Tape: Insulating tape may be applied over the terminal for further protection and sealing.
Typical Technical Data Associated with Medium Voltage Cable Heat Shrink Terminals:
Voltage Rating: Specifies the range of voltages that the terminal is designed to handle, usually expressed in kilovolts (kV). Common voltage ratings for medium voltage terminals might be 6 kV, 11 kV, 20 kV,or 33 kV.
Temperature Range: Indicates the operating temperature range that the terminal can withstand without degradation of its electrical or mechanical properties.
Shrink Ratio: Specifies how much the heat shrink tubing will shrink when heated. For example, a shrink ratio of 3:1 means the tubing will shrink to one-third of its original size.
Dielectric Strength: This refers to the maximum electric field that the insulation material can withstand without breaking down. It's typically measured in volts per unit thickness (e.g., kV/mm).
Tensile Strength: Indicates how much force the terminal can withstand before breaking. Expressed in pounds per square inch (psi) or Newtons per square millimeter (N/mm²).
Elongation at Break: Measures how much the terminal can stretch before breaking, expressed as a percentage.
Water Absorption: The amount of water the terminal material can absorb over time, which can affect its insulating properties.
Flame Retardancy: Some terminals may be designed to have flame-retardant properties to enhance safety.
- Previous:No
- Next:No
Related Products



 info@dosensecable.com
info@dosensecable.com









 Tel:
Tel:  Address: Zhengzhou, Henan,China
Address: Zhengzhou, Henan,China